www.huvitera.ee/arduino-led
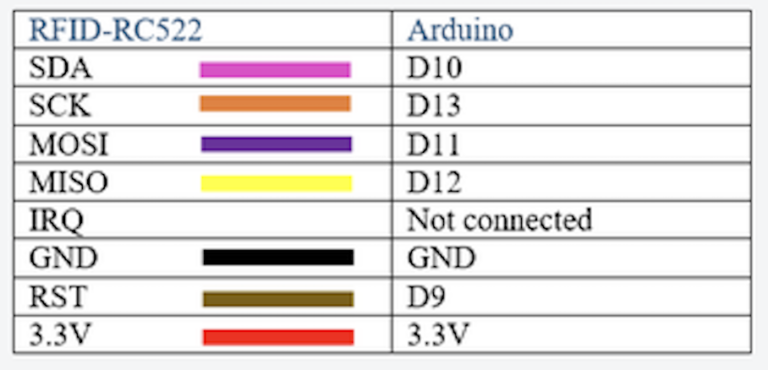
// NR1 - LCD, I2C ja RFID - leia ekraanilt oma kaardi kood
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#define SS_PIN 10
#define RST_PIN 9
#define LED_DENIED_PIN 7
#define LED_ACCESS_PIN 6
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x3F,16,2);
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // Instance of the class
int code[] = {32,154,149,117}; //This is the stored UID (Unlock Card)
int codeRead = 0;
String uidString;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522
Serial.println("Arduino RFID reading UID");
pinMode( LED_DENIED_PIN , OUTPUT);
pinMode( LED_ACCESS_PIN , OUTPUT);
lcd.init();
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Show your card:)");
}
void loop() {
if ( mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent())
{
if ( mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial())
{
lcd.clear();
Serial.print("Tag UID:");
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Tag UID:");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
for (byte i = 0; i < mfrc522.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
lcd.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
lcd.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
// lcd.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
int i = 0;
boolean match = true;
while(i<mfrc522.uid.size)
{
if(!(int(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i]) == int(code[i])))
{
match = false;
}
i++;
}
delay(3000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
}
}
}
void reset_state()
{
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Show your card:)");
digitalWrite( LED_ACCESS_PIN , LOW);
digitalWrite( LED_DENIED_PIN , LOW);
}
// NR2 - Koodi muutmine numbriteks, õpetajale edastamine
Convert HEX to DECIMAL
https://www.atatus.com/tools/hex-to-decimal
// NR3 - LED vilkumine
#include <FastLED.h>
#define DATA_PIN 5
#define NUM_LEDS 100
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
void setup() {
FastLED.addLeds<NEOPIXEL, DATA_PIN>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
}
void loop() {
// Set all LEDs to red
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Red);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
// Set all LEDs to green
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Green);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
// Set all LEDs to blue
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Blue);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
}
// NR4 - LCD ja RFID, LED
#include <FastLED.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#define SS_PIN 10
#define RST_PIN 9
#define DATA_PIN 5
#define NUM_LEDS 100
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define LED_DENIED_PIN 7
#define LED_ACCESS_PIN 6
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x3F,16,2);
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // Instance of the class
int code[] = {98, 101, 31, 31}; //This is the stored UID (Unlock Card)
int codeRead = 0;
String uidString;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522
Serial.println("Arduino RFID reading UID");
pinMode( LED_DENIED_PIN , OUTPUT);
pinMode( LED_ACCESS_PIN , OUTPUT);
lcd.init();
FastLED.addLeds<NEOPIXEL, DATA_PIN>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Show your card:)");
}
void loop() {
if ( mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent())
{
if ( mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial())
{
lcd.clear();
Serial.print("Tag UID:");
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Tag UID:");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
for (byte i = 0; i < mfrc522.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
lcd.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
lcd.print(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
// lcd.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
int i = 0;
boolean match = true;
while(i<mfrc522.uid.size)
{
if(!(int(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i]) == int(code[i])))
{
match = false;
}
i++;
}
delay(3000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
if(match)
{
digitalWrite( LED_ACCESS_PIN , HIGH);
lcd.print("Authorized access");
for (int i = 0; i <= 99; i++) {
leds[i] = CRGB ( 0, 0, 255);
FastLED.show();
delay(40);
}
for (int i = 99; i >= 0; i--) {
leds[i] = CRGB ( 0, 255, 0);
FastLED.show();
delay(20);
}
delay(2000);
// Set all LEDs to green
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Green);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Green);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Green);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
}else{
digitalWrite( LED_DENIED_PIN , HIGH);
lcd.print(" Access denied ");
Serial.println("\nUnknown Card");
for (int i = 0; i <= 99; i++) {
leds[i] = CRGB ( 0, 0, 255);
FastLED.show();
delay(40);
}
for (int i = 99; i >= 0; i--) {
leds[i] = CRGB ( 255, 0, 0);
FastLED.show();
delay(20);
}
delay(2000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Red);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Red);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Red);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("============================");
mfrc522.PICC_HaltA();
delay(3000);
reset_state();
}
}
}
void reset_state()
{
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Show your card:)");
digitalWrite( LED_ACCESS_PIN , LOW);
digitalWrite( LED_DENIED_PIN , LOW);
}
// NR5 - LED vilkumised
#include <FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 5
#define NUM_LEDS 300
#define BRIGHTNESS 64
#define LED_TYPE WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define UPDATES_PER_SECOND 100
// This example shows several ways to set up and use 'palettes' of colors
// with FastLED.
//
// These compact palettes provide an easy way to re-colorize your
// animation on the fly, quickly, easily, and with low overhead.
//
// USING palettes is MUCH simpler in practice than in theory, so first just
// run this sketch, and watch the pretty lights as you then read through
// the code. Although this sketch has eight (or more) different color schemes,
// the entire sketch compiles down to about 6.5K on AVR.
//
// FastLED provides a few pre-configured color palettes, and makes it
// extremely easy to make up your own color schemes with palettes.
//
// Some notes on the more abstract 'theory and practice' of
// FastLED compact palettes are at the bottom of this file.
CRGBPalette16 currentPalette;
TBlendType currentBlending;
extern CRGBPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette;
extern const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM;
void setup() {
delay( 3000 ); // power-up safety delay
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
currentPalette = RainbowColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
void loop()
{
ChangePalettePeriodically();
static uint8_t startIndex = 0;
startIndex = startIndex + 1; /* motion speed */
FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( startIndex);
FastLED.show();
FastLED.delay(1000 / UPDATES_PER_SECOND);
}
void FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( uint8_t colorIndex)
{
uint8_t brightness = 255;
for( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette( currentPalette, colorIndex, brightness, currentBlending);
colorIndex += 3;
}
}
// There are several different palettes of colors demonstrated here.
//
// FastLED provides several 'preset' palettes: RainbowColors_p, RainbowStripeColors_p,
// OceanColors_p, CloudColors_p, LavaColors_p, ForestColors_p, and PartyColors_p.
//
// Additionally, you can manually define your own color palettes, or you can write
// code that creates color palettes on the fly. All are shown here.
void ChangePalettePeriodically()
{
uint8_t secondHand = (millis() / 1000) % 60;
static uint8_t lastSecond = 99;
if( lastSecond != secondHand) {
lastSecond = secondHand;
if( secondHand == 0) { currentPalette = RainbowColors_p; currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 10) { currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p; currentBlending = NOBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 15) { currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p; currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 20) { SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette(); currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 25) { SetupTotallyRandomPalette(); currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 30) { SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette(); currentBlending = NOBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 35) { SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette(); currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 40) { currentPalette = CloudColors_p; currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 45) { currentPalette = PartyColors_p; currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 50) { currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p; currentBlending = NOBLEND; }
if( secondHand == 55) { currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p; currentBlending = LINEARBLEND; }
}
}
// This function fills the palette with totally random colors.
void SetupTotallyRandomPalette()
{
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
currentPalette[i] = CHSV( random8(), 255, random8());
}
}
// This function sets up a palette of black and white stripes,
// using code. Since the palette is effectively an array of
// sixteen CRGB colors, the various fill_* functions can be used
// to set them up.
void SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette()
{
// 'black out' all 16 palette entries...
fill_solid( currentPalette, 16, CRGB::Black);
// and set every fourth one to white.
currentPalette[0] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[4] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[8] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[12] = CRGB::White;
}
// This function sets up a palette of purple and green stripes.
void SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette()
{
CRGB purple = CHSV( HUE_PURPLE, 255, 255);
CRGB green = CHSV( HUE_GREEN, 255, 255);
CRGB black = CRGB::Black;
currentPalette = CRGBPalette16(
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black,
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black );
}
// This example shows how to set up a static color palette
// which is stored in PROGMEM (flash), which is almost always more
// plentiful than RAM. A static PROGMEM palette like this
// takes up 64 bytes of flash.
const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM =
{
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray, // 'white' is too bright compared to red and blue
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Black
};
// Additionl notes on FastLED compact palettes:
//
// Normally, in computer graphics, the palette (or "color lookup table")
// has 256 entries, each containing a specific 24-bit RGB color. You can then
// index into the color palette using a simple 8-bit (one byte) value.
// A 256-entry color palette takes up 768 bytes of RAM, which on Arduino
// is quite possibly "too many" bytes.
//
// FastLED does offer traditional 256-element palettes, for setups that
// can afford the 768-byte cost in RAM.
//
// However, FastLED also offers a compact alternative. FastLED offers
// palettes that store 16 distinct entries, but can be accessed AS IF
// they actually have 256 entries; this is accomplished by interpolating
// between the 16 explicit entries to create fifteen intermediate palette
// entries between each pair.
//
// So for example, if you set the first two explicit entries of a compact
// palette to Green (0,255,0) and Blue (0,0,255), and then retrieved
// the first sixteen entries from the virtual palette (of 256), you'd get
// Green, followed by a smooth gradient from green-to-blue, and then Blue.

